
AFRILCATE
WHAT IS RADIANT ENERGY?
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic waves.
It can be described in terms of discrete packets of energy, called photons or continuous electromagnetic waves.
Radiant energy is also a type of kinetic energy since it involves the motion of energy in waveform or particle.
FORMS OF RADIANT ENERGY
Since radiant energy is energy emitted from electromagnetic radiations, it can take various forms.
It can exist in the form of
- visible waves -which we call light energy
- invisible waves such as micro waves, x-rays or infrared waves.

sunlight – a type of visible light
HOW IS RADIANT ENERGY PRODUCED?
Radiant energy is produced from oscillating charges.
This oscillating motion produces electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other.
The electric and magnetic fields are also perpendicular to the direction the wave travels.
Therefore, an electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave.
They are different kinds of electromagnetic waves and all of them have different wavelengths and energies.
The shorter the wavelength, the higher its energy.
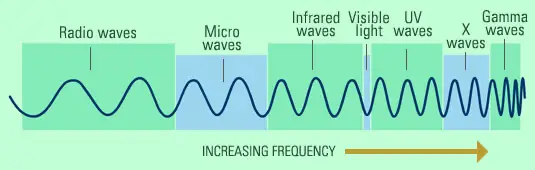
electromagnetic spectrum
The radiant energy is stored in the electric and magnetic fields.
HOW DO RADIANT ENERGY TRAVEL?
Radiant energy can travel through any substance and also through space.
It does not need any material medium for its propagation.
Radiant energy propagates outwards from the source and travels at the speed of light.
EXAMPLES OF RADIANT ENERGY
- Sunlight – the sun is the biggest source of radiant energy.
- Microwave – utilizes radiant energy to heat up our food.
- Mobile phones – utilizes radiant energy to function.
- Infrared radiation
- X-rays – emits radiant energy
- Light from bulbs
- All forms of visible light
- Heat emitted from a stove or burner
- Heat from burning wood/campfire

light from bulb
USES OF RADIANT ENERGY
Radiant energy is utilized in the medical and telecommunication fields.
It is also harnessed for power production.
Some specific uses of radiant energy include:
- For Radiant heating
- As a medium of communication
- Utilized by plants to produce their food (photosynthesis)
- For medical treatment and inspection
- For separation and sorting
- For solar energy
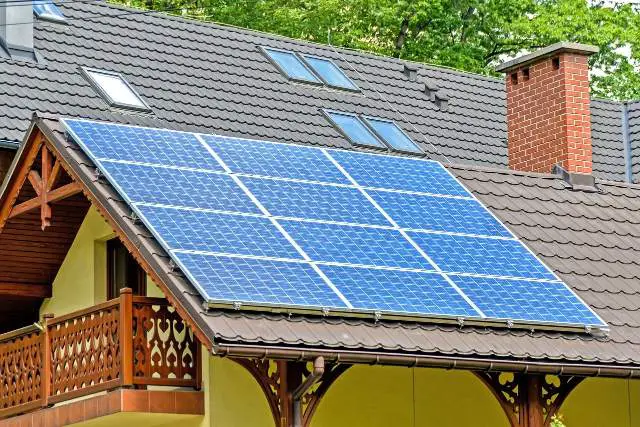

solar system
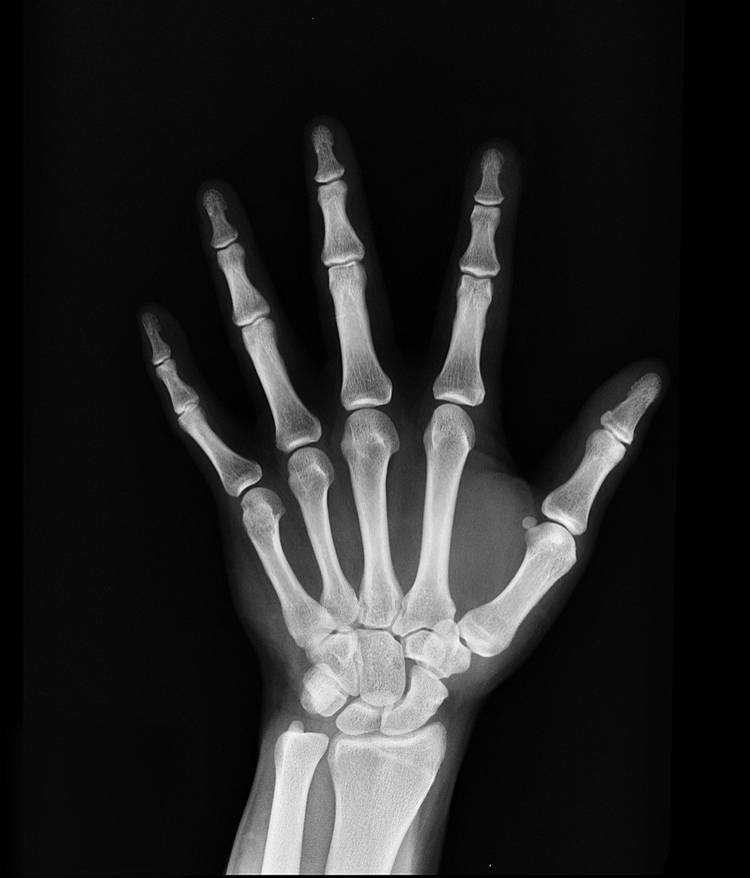
x-ray
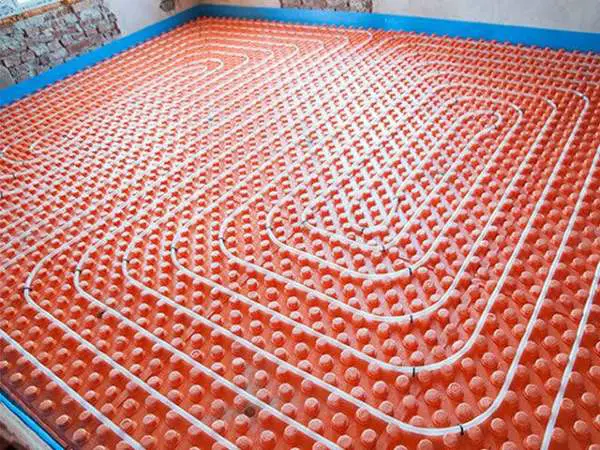

underfloor heating

