
AFRILCATE
WHAT IS CONDENSATION?
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from the gaseous phase to the liquid phase.
It is a process in which water vapor in the air changes into liquid water when it comes in contact with a cooler surface.
Let’s relate this with a real-life scenario.
Imagine that you are having a hot shower. If you take a look at the mirror after the bath, you will notice that the mirror is covered with fog and you can’t clearly see your reflection.
Try wiping the steamy fog from the mirror and you will notice that they are nothing but tiny water beads.
The water vapor which is at an elevated temperature, cooled down when it came in contact with the mirror which happens to be at a much more reduced temperature.
This cool surface changes the water vapor in the surrounding to tiny water droplets visible on the mirror.
This phenomenon is known as condensation.

WHAT CAUSES CONDENSATION?
Condensation is caused by a change in pressure and temperature of water vapor.
It occurs when:
- a vapor is cooled or pressured to its saturation limit.
- when the molecular density in the gas phase reaches its maximal threshold.
- water vapor comes in contact with hygroscopic condensation nuclei in the atmosphere.
In free air, condensation occurs due to the presence of tiny particles (about 0.2 – 10.0 microns) light enough to remain suspended in the air.
These micro-particles are called condensation nuclei.
Condensation nuclei are formed from a variety of water nucleates including dust, smoke, pollen, salt from ocean spray and sulfates.
They provide surfaces upon which water vapor can condense to create cloud droplets.
Condensation is largely dependent upon the amount of cooling and the relative humidity of the air.
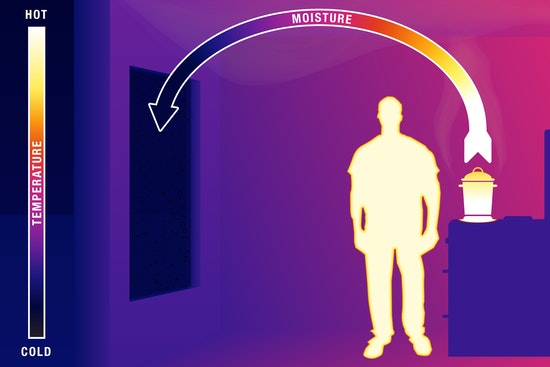
CONDENSATION PROCESS
Just like any other matter, water also consists of molecules.
In a vapor form, the molecules are energetic, fast-moving and far apart.
As the vapor encounters cooler temperatures, the molecules become slower, less energetic and closer together.
Subsequently, the vapor turns into liquid upon reaching a threshold energy level.
CONDENSATION HOME EXPERIMENT
Anyone can demonstrate the process of condensation through an easy experiment.
All you need is just two cups and hot water.
Let’s get started…
- Fill one cup half-level with the hot water.
- Observe the steam gushing out of the hot water.
- Now, take the other cup, flip it upside down, and carefully put it on top of the half-filled cup.
- Wait for 5 mins, and take 2nd cup down.
You will see that the steam condenses back to liquid at the top surface of the 2nd cup when placed upside down.
As condensation occurs, the water molecules become closely packed and this results in the release of heat to the atmosphere.
EXAMPLES OF CONDENSATION
You don’t have to look at something as far away as the cloud to notice condensation.
It is a daily occurrence and everywhere around us.
Some examples of condensation phenomenon include:
- Droplets on can or bottle: Having a cold soda on a hot day, the can “sweats.” Water molecules in the air as a vapor hit the colder surface of the can and turn into liquid water.
- Morning Dew: Dew forms in the morning on leaves and grass because of the warmer air deposits water molecules on the cool leaves.
- Foggy windshield: When you get in your car in the morning and are breathing warmer air, the warm air comes into contact with the cooler windshield and forms a foggy window.
- Foggy mirror: The mirror in the bathroom during a warm shower becomes foggy because warmer water vapor in the air hits the cooler surface of the mirror.
- Clouds: Clouds form by condensation, warmer air comes into contact with cooler dust particles and the vapor deposits into a liquid on those particles forming clouds.

morning dew on plants
DO YOU KNOW?
Vapor cooling and compressing equipment that collects condensed liquids is called a “condenser”.
The reverse of condensation is vaporization.
DO YOU KNOW?
Vapor cooling and compressing equipment that collects condensed liquids is called a “condenser”.
The reverse of condensation is vaporization.

