Coefficient of Kinetic Friction (Fully Explained)
written by Stanley Udegbunam ||updated Oct 22, 2020
Overview
What is Coefficient of kinetic friction?
The coefficient of kinetic friction is a numerical value that quantifies the friction intensity of a sliding surface relative to another.
Also known as kinetic friction coefficient, it measures the extent of material grip between a moving object and its contact surface.
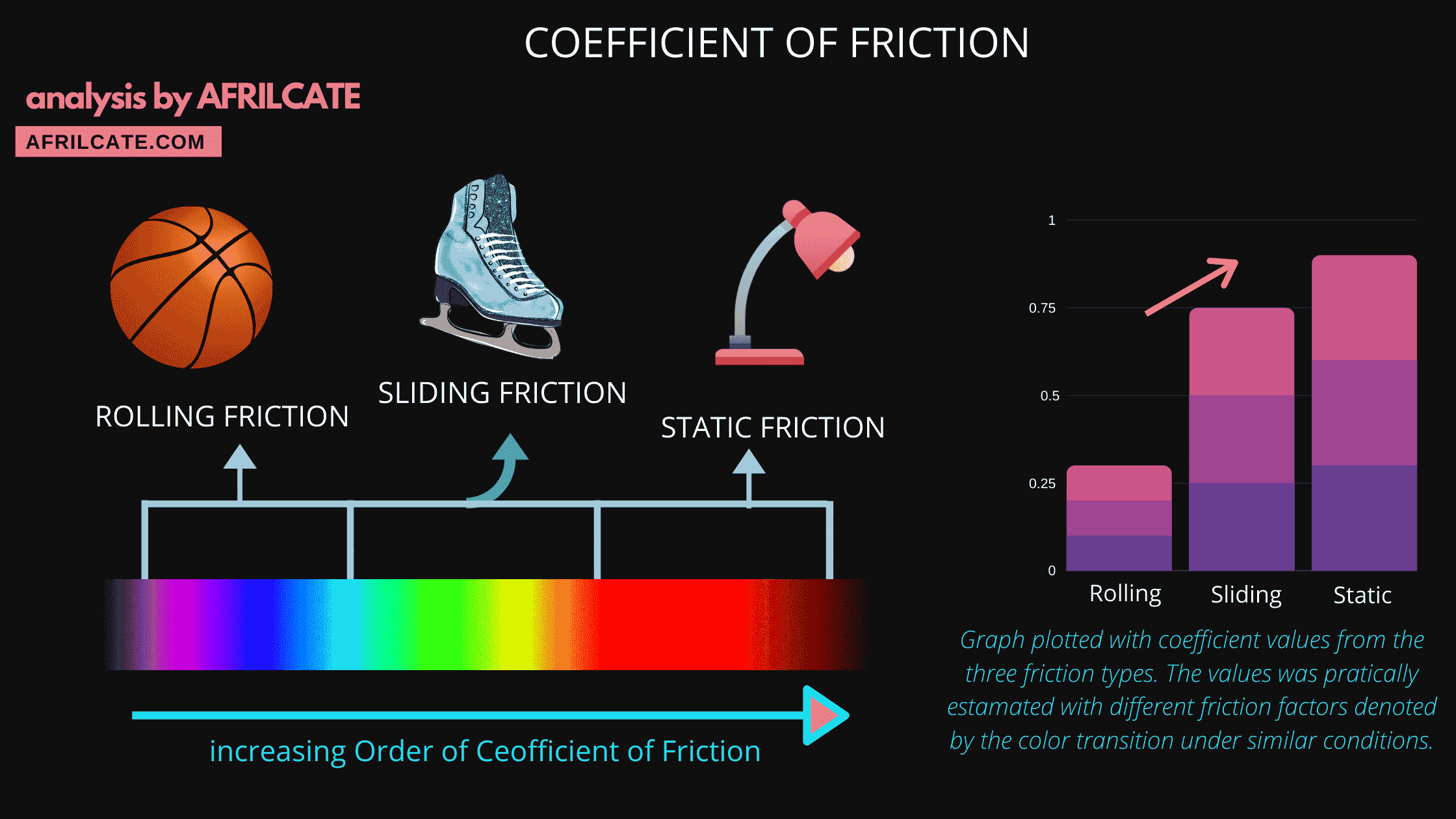
Recall that there are three types of dry friction: Static friction, kinetic friction, and rolling friction.
Although the coefficient of kinetic friction is higher than of rolling friction, it’s still less than the coefficient of static friction.
This is because the force of static friction is greater than both kinetic and rolling friction.
Therefore more force is required to initiate motion when an object is at rest but once the motion is initiated, less force will be required to maintain the motion.
Rolling objects usually have the least friction coefficient due to its minimal contact area.
Formula for Coefficient of kinetic friction
Kinetic friction coefficient is denoted with µs.
The formula for the coefficient of kinetic friction is given by;
| µk = Fk/N |
Where,
- Fk is the force of kinetic friction
- N is the normal force, sometimes it’s denoted by η
The Normal force has the same magnitude as the weight.
It’s represented by the equation; N = m x g
If the object or plane is inclined at an angle (∅), the normal force becomes:
N = m gcos∅
Where m = mass of the object.
And g = acceleration due to gravity.
F and N are measured in units of force (such as Newton or pound).
Since friction is a force, the unit of the frictional force is the newton (N).
The coefficient of kinetic friction is unitless.
How to find the Coefficient of kinetic friction
To find the coefficient of kinetic friction, we will use the formula above to carry out some friction coefficient calculations.
Calculations on Coefficient of kinetic friction
Example 1
A total force of 20N is required to move a 5 kg block along a horizontal wooden surface.
If the acceleration due to gravity is estimated to be 10 m/s2, calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction.
solution
Friction force (Fk ) = 20N
mass (m) = 5kg
g = 10 m/s2
Fk = µk x N
µk = Fk / N
µk = Fk/m x g = 20/(5×10) = 20/50 = 0.4
therefore the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.4
Example 2
A 3kg stainless cup is pushed across a horizontal glass table with µk = 0.6
Calculate the kinetic friction force given that g = 9.81 m/s2.
Solution
Fk = µkN
but N = m x g
Fk = µk mg
Fk = 0.6 x 3 x 9.81
Fk = 17.66 N
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
The force acting on a moving train is 280N.
If the kinetic friction is 115N, determine the kinetic friction coefficient.
a.) 0.32
X wrong!!
b.) 0.41
✔ Correct
c.) 0.57
X wrong!!
d.) none of the above
X wrong!!
SHOW SOLVING
The correct option is b. 0.41
µk = Fk/N
µk = 115/280 = 0.41
Comprehensive List of Kinetic friction Coefficients
The list below is a long list of kinetic friction coefficients of different materials measured under different surface conditions.
The greasy surface condition represents any form of lubrication.
C.O.K-F —- Coefficient of Kinetic friction
Scroll sideways to view the complete list
Material 1 | Material 2 | Coefficient of Kinetic Friction | |
DRY | GREASY | ||
Aluminum | Aluminum | 1.4 | - |
Aluminum | Mild Steel | 0.47 | - |
Brass | Cast Iron | 0.3 | - |
Bronze | Cast Iron | 0.22 | - |
Cadmium | Mild Steel | 0.46 | - |
Cast Iron | Cast Iron | 0.15 | 0.07 |
Cast Iron | Oak | 0.49 | 0.075 |
Copper | Cast Iron | 0.29 | - |
Copper | Mild Steel | 0.36 | 0.18 |
Copper | Steel (304 stainless) | 0.21 | - |
Copper | Steel | 0.8 | - |
Glass | Glass | 0.4 | 0.09 - 0.12 |
Glass | Nickel | 0.56 | - |
Lead | Cast Iron | 0.43 | - |
Lead | Steel | 1.4 | - |
Nickel | Nickel | 0.53 | 0.12 |
Nickel | Mild Steel | 0.64 | 0.178 |
Oak | Oak (parallel grain) | 0.48 | - |
Oak | Oak (cross grain) | 0.32 | 0.072 |
Rubber | Asphalt (Dry) | 0.5 - 0.8 | - |
Rubber | Asphalt (Wet) | 0.25- 0.75 | - |
Rubber | Concrete (Dry) | 0.6 - 0.85 | - |
Rubber | Concrete (Wet) | 0.45 - 0.75 | - |
Steel(Mild) | Brass | 0.44 | - |
Steel (Mild) | Cast Iron | 0.23 | 0.133 |
Steel | Copper Lead Alloy | - | 0.145 |
Steel (Mild) | Lead | 0.95 | 0.3 |
Steel (Mild) | Phos. Bros | 0.34 | 0.173 |
Steel (Mild) | Steel (Mild) | 0.57 | 0.09-0.19 |
Steel(Hard) | Steel (Hard) | 0.42 | 0.029-0.12 |
Teflon | Steel | - | 0.04 |
Teflon | Teflon | - | 0.04 |
Tin | Cast Iron | 0.32 | - |
Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | Aluminium Alloy 6061-T6 | 0.38 | - |
Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | 0.30 | - |
Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | Bronze | 0.27 | - |
Zinc | Cast Iron | 0.21 | - |
MATERIAL 1 | MATERIAL 2 | C. O. K-F (DRY) | C. O. K-F(GREASY) |
Aluminum | Aluminum | 1.4 | - |
Aluminum | Mild Steel | 0.47 | - |
Brass | Cast Iron | 0.3 | - |
Bronze | Cast Iron | 0.22 | - |
Cadmium | Mild Steel | 0.46 | - |
Cast Iron | Cast Iron | 0.15 | 0.07 |
Cast Iron | Oak | 0.49 | 0.075 |
Copper | Cast Iron | 0.29 | - |
Copper | Mild Steel | 0.36 | 0.18 |
Copper | Steel (304 stainless) | 0.21 | - |
Copper | Steel | 0.8 | - |
Glass | Glass | 0.4 | 0.09 - 0.12 |
Glass | Nickel | 0.56 | - |
Lead | Cast Iron | 0.43 | - |
Lead | Steel | 1.4 | - |
Nickel | Nickel | 0.53 | 0.12 |
Nickel | Mild Steel | 0.64 | 0.178 |
Oak | Oak (parallel grain) | 0.48 | - |
Oak | Oak (cross grain) | 0.32 | 0.072 |
Rubber | Asphalt (Dry) | 0.5 - 0.8 | - |
Rubber | Asphalt (Wet) | 0.25- 0.75 | - |
Rubber | Concrete (Dry) | 0.6 - 0.85 | - |
Rubber | Concrete (Wet) | 0.45 - 0.75 | - |
Steel(Mild) | Brass | 0.44 | - |
Steel (Mild) | Cast Iron | 0.23 | 0.133 |
Steel | Copper Lead Alloy | - | 0.145 |
Steel (Mild) | Lead | 0.95 | 0.3 |
Steel (Mild) | Phos. Bros | 0.34 | 0.173 |
Steel (Mild) | Steel (Mild) | 0.57 | 0.09-0.19 |
Steel(Hard) | Steel (Hard) | 0.42 | 0.029-0.12 |
Teflon | Steel | - | 0.04 |
Teflon | Teflon | - | 0.04 |
Tin | Cast Iron | 0.32 | - |
Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | Aluminium Alloy 6061-T6 | 0.38 | - |
Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | 0.30 | - |
Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V(Grade 5) | Bronze | 0.27 | - |
Zinc | Cast Iron | 0.21 | - |
table extracted from internet archive
Frequently Asked Questions on Kinetic Friction Coefficient
1. What’s the coefficient of kinetic friction of wood on wood?
Ans: 0.2 (refer to the table above)
2. What’s the coefficient of kinetic friction between rubber and asphalt?
Ans: The coefficient of kinetic friction between rubber and asphalt ranges between 0.5 – 0.8 (dry asphalt) and 0.25-0.75 (wet asphalt)
Ans: 0.25 – 0.5 (refer to table above)
3. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between steel and teflon?
Ans: The coefficient of steel and teflon is 0.04 for greasy surface condition. (refer to table)
4. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between glass and nickel.
Ans: The coefficient of kinetic friction between glass and nickel is 0.56
Now…Over to you
What do you think about this article?
was it helpful in any way and would you like to see more content like this?
Share your thoughts and answers with us in the comment section below.

